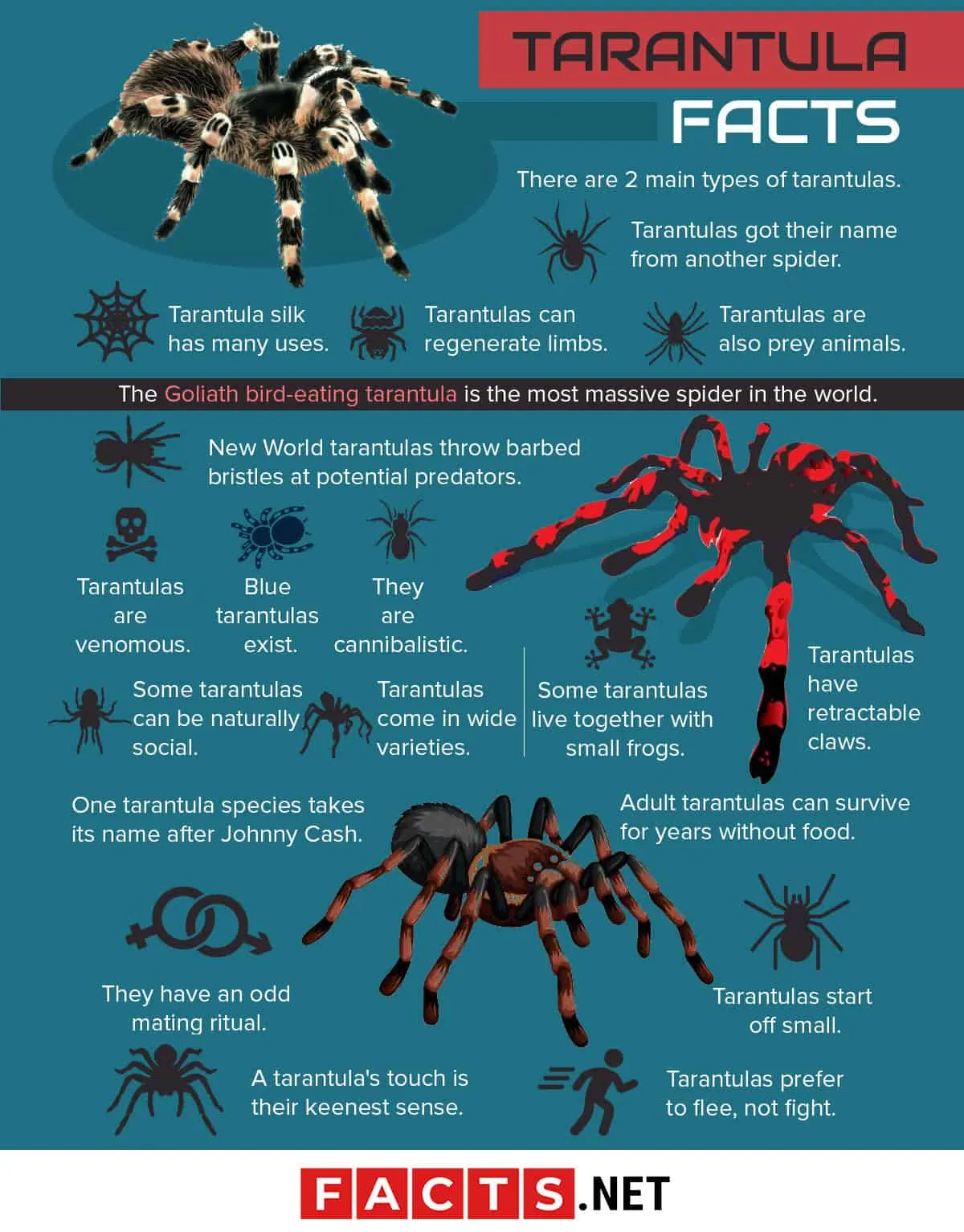
What is the Nevada Tarantula?
The Nevada tarantula, a fascinating arachnid, is a prominent inhabitant of the Mojave Desert and surrounding regions. These large, hairy spiders are a significant part of the local ecosystem, playing a role in controlling insect populations and serving as a food source for other animals. Despite their imposing appearance, they are generally not aggressive towards humans, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their presence is an indicator of a healthy desert environment, and understanding their behavior and habitat is crucial for their conservation. These creatures have adapted to the harsh desert conditions, showcasing remarkable survival strategies. The Nevada tarantula’s life cycle, from egg to adult, is a testament to their resilience and adaptability. They are an integral part of the Nevada desert’s biodiversity, and learning more about them can increase awareness of the need for their protection. They are an essential part of the desert ecosystem, playing a vital role in maintaining ecological balance.
Species Found in Nevada
Several species of tarantulas can be found within the state of Nevada. The most common is the Aphonopelma chalcodes, often referred to as the desert blonde tarantula. These spiders are well-suited to the arid climate and are frequently encountered by residents and visitors. Other less common species might also exist in certain microhabitats, but comprehensive surveys are often difficult due to their nocturnal habits and the vastness of their habitat. The specific distribution can vary depending on factors like elevation, vegetation, and the availability of prey. Each species has its unique characteristics, behaviors, and ecological roles. Understanding these differences is important for conservation efforts and for appreciating the diversity of life in the Nevada desert. It’s important to consult with local wildlife experts for precise species identification.
Characteristics of Nevada Tarantulas
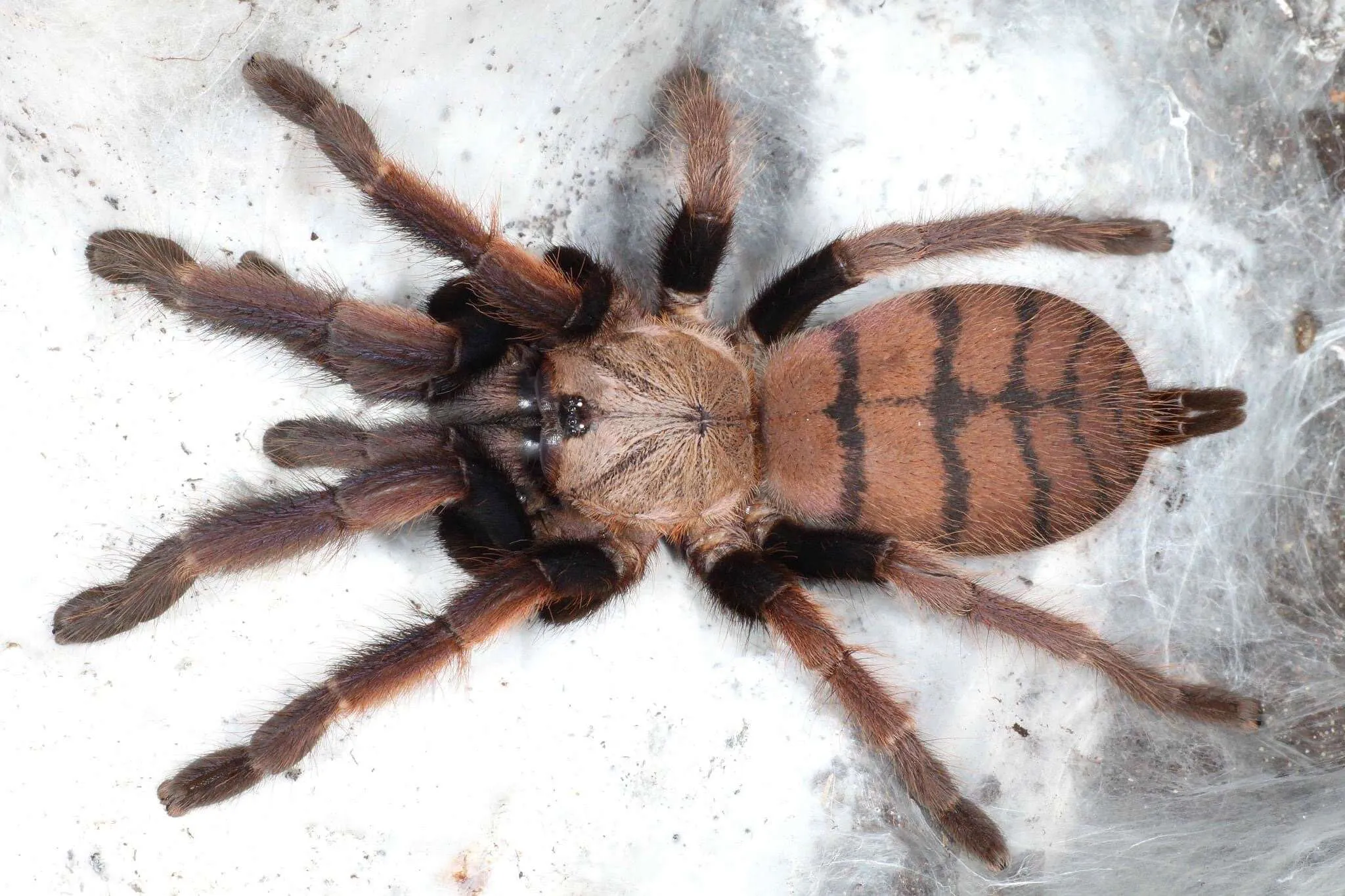

Size and Appearance
Nevada tarantulas are known for their large size, with body lengths that can reach up to 2.5 inches, and leg spans sometimes exceeding 5 inches. Their bodies are covered in dense, bristly hairs, giving them a fuzzy appearance. Their coloration typically blends well with their surroundings, providing camouflage. The females are generally larger than the males, a common characteristic among tarantula species. Their impressive size and distinctive appearance often make them a memorable sight for those who encounter them. The overall appearance helps them blend seamlessly into their desert habitat, helping them to evade predators. Their physical attributes are a result of evolutionary adaptations.
Color Variations
The color of Nevada tarantulas can vary, but they are often shades of brown, tan, or beige, which provide excellent camouflage in the desert environment. Some individuals may have slightly reddish or golden hues, while others are more muted. The specific color can depend on factors like the individual spider’s genetics, age, and the environmental conditions of its habitat. The variation in color helps them blend in with the sand, rocks, and sparse vegetation of their surroundings. This camouflage is essential for both hunting and avoiding predators. These subtle differences in appearance make them unique. The coloration can vary depending on the specific species and the individual’s environment.
The Nevada Tarantula Habitat
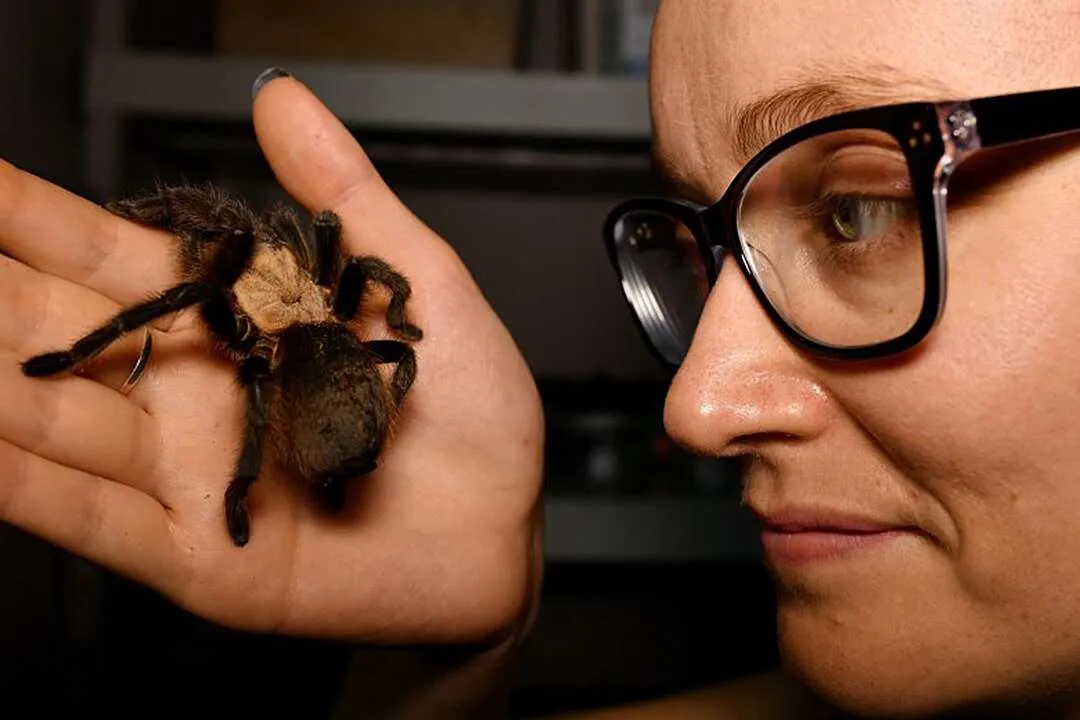

Preferred Environments
Nevada tarantulas prefer arid and semi-arid environments, specifically the desert and scrublands of the Southwestern United States. They are often found in areas with sparse vegetation, sandy or rocky soils, and access to burrows. They construct their homes in the ground, either by digging their own burrows or by occupying abandoned rodent burrows. The specific habitat requirements can vary depending on the species, but generally, they prefer areas that offer protection from the elements and provide ample hunting grounds. The availability of suitable burrows and a consistent food supply are crucial for their survival. They also need a temperature range that they can thrive in. They are well-adapted to the extreme environmental conditions.
Adaptations to the Desert
These spiders have developed remarkable adaptations to thrive in the harsh desert environment. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid the intense daytime heat, and they are most active during the cooler evenings. They can conserve water efficiently, extracting moisture from their prey and minimizing water loss through their exoskeletons. Their burrowing behavior provides shelter from the sun and protection from predators. They are also well-adapted to withstand periods of drought, enabling them to survive when food is scarce. These adaptations highlight the remarkable resilience of Nevada tarantulas.
Nevada Tarantula Behavior
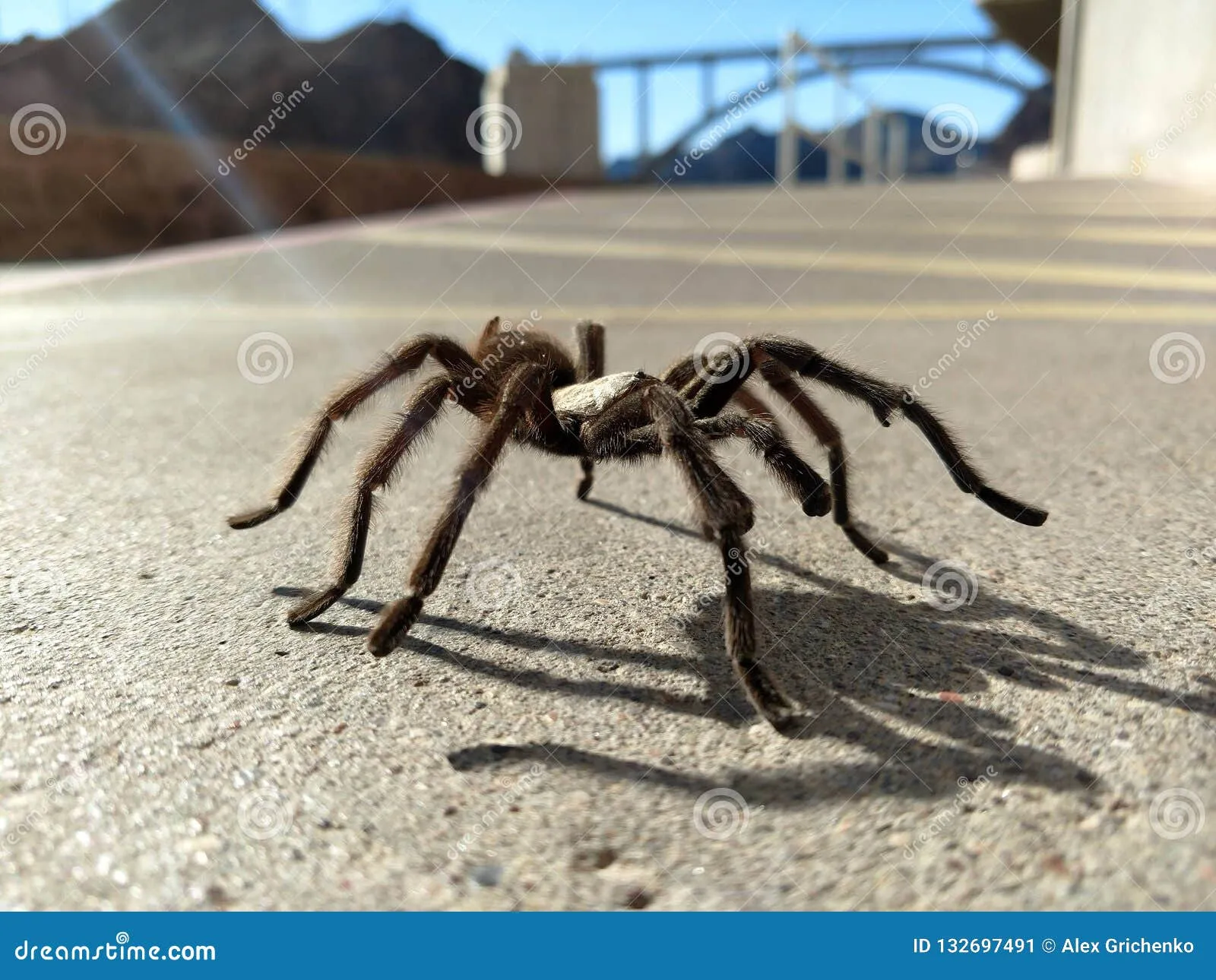

Diet and Feeding Habits
Nevada tarantulas are primarily carnivores, feeding on a variety of insects, other spiders, and occasionally small vertebrates. They are ambush predators, waiting patiently in or near their burrows for prey to come within striking distance. Once a suitable target is detected, they quickly pounce, injecting venom to immobilize and begin the digestion process. Their diet consists mainly of crickets, beetles, grasshoppers, and other insects, but larger individuals may consume small lizards or mice. They have a potent venom that helps in capturing their prey. The hunting behavior is an interesting survival strategy.
Defensive Mechanisms
When threatened, Nevada tarantulas have several defensive mechanisms. They may flick urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause irritation to the skin and eyes of potential predators. They can also bite, though their venom is not generally considered life-threatening to humans. They usually try to escape if they feel threatened. The defensive behaviors are a last resort, used to protect themselves from harm. The effectiveness of these mechanisms helps them survive in the wild. They usually prefer to retreat, but will defend themselves when cornered.
Population and Conservation

Threats to Nevada Tarantula Populations
Several factors can threaten Nevada tarantula populations. Habitat loss due to urbanization, agriculture, and other forms of development is a major concern. The use of pesticides can also affect their prey base and directly harm the spiders. Climate change, with its potential impacts on desert ecosystems, poses a growing threat. Illegal collecting for the pet trade can also negatively impact local populations. Understanding these threats is essential for developing effective conservation strategies. It is important to protect their natural habitats. The survival of these creatures depends on these factors.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts focused on protecting Nevada tarantulas include habitat preservation, educational initiatives, and research. Protecting and restoring desert habitats is crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of these spiders. Raising public awareness about their importance and dispelling common misconceptions can help reduce human-caused threats. Supporting scientific research to better understand their biology, behavior, and population dynamics is also essential. Effective conservation requires a collaborative approach involving government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities. These conservation methods will help the population of these spiders thrive.
Interesting Facts About Nevada Tarantulas
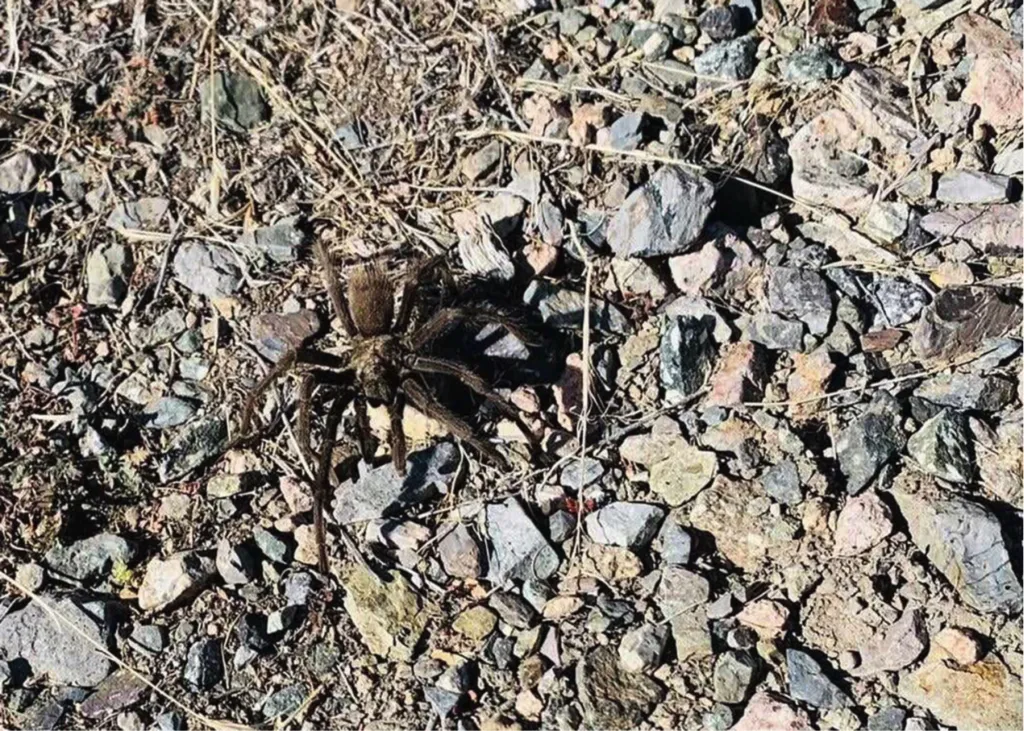

Lifespan
Nevada tarantulas can live for a surprisingly long time. Females often have a lifespan of 20-30 years, while males typically live for a shorter period, usually 7-10 years. This difference in lifespan is common among tarantula species and is influenced by factors like their reproductive cycle and the challenges of the environment. Their longevity adds to their mystique and highlights the adaptability of these desert creatures. The long life cycle of the females makes them a prominent part of the desert ecosystem.
Venom
The venom of the Nevada tarantula is not considered highly dangerous to humans. A bite may cause some pain, redness, and swelling at the bite site, but it is rarely life-threatening. Their venom is primarily used to subdue prey. If bitten, it’s recommended to clean the area and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen. Understanding the effects of their venom can help in managing encounters with these spiders. The primary purpose of the venom is to assist in hunting. The venom is not a major risk for humans.
Conclusion
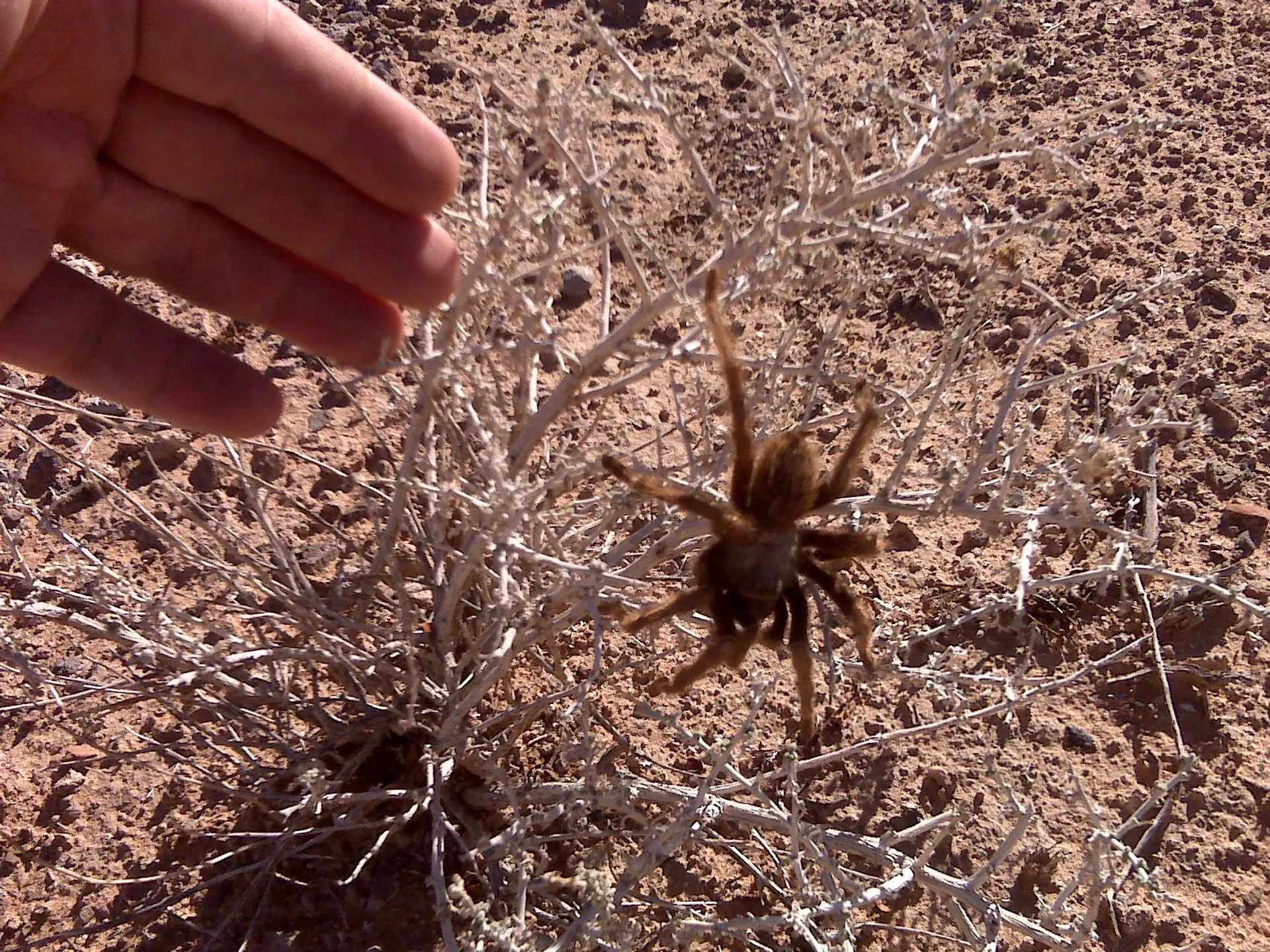

The Nevada tarantula is a fascinating and integral part of the desert ecosystem. Understanding their characteristics, habitat, behavior, and the threats they face is essential for their conservation. By appreciating their role in the environment and supporting conservation efforts, we can help ensure that these remarkable creatures continue to thrive in their natural habitat. It’s important to respect and protect these creatures for future generations. The Nevada tarantula is a testament to the wonders of the natural world.